Introduction
The effects of climate change are increasingly becoming a major concern for global economies. From extreme weather events like hurricanes and droughts to shifts in agricultural productivity and energy consumption, climate change is influencing every aspect of business and government policy. As the world grapples with the escalating effects of global warming, the need for a comprehensive approach to mitigate its economic impacts has never been more urgent.
In this article, we’ll explore how climate change is impacting global economies, the challenges it presents across various industries, and the strategies being employed to mitigate these impacts. Whether you’re a policymaker, business leader, or consumer, understanding the economic consequences of climate change is critical for navigating this new era.
1. Understanding Climate Change and Its Effects
What is Climate Change?
Climate change refers to long-term shifts in temperature, precipitation, and other atmospheric conditions on Earth. While natural factors have contributed to climate variations over time, human activities—particularly the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation—have accelerated the process, leading to higher concentrations of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
The global temperature has risen significantly since the industrial revolution, and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) warns that continuing trends could lead to catastrophic impacts on ecosystems and economies if not addressed.
How Climate Change Affects Natural Resources
The impacts of climate change are most visibly felt in natural resources. From rising sea levels to shrinking glaciers, these changes affect the availability of resources like water and land that are vital for industries such as agriculture, fishing, and manufacturing.
Extreme Weather Events and Natural Disasters
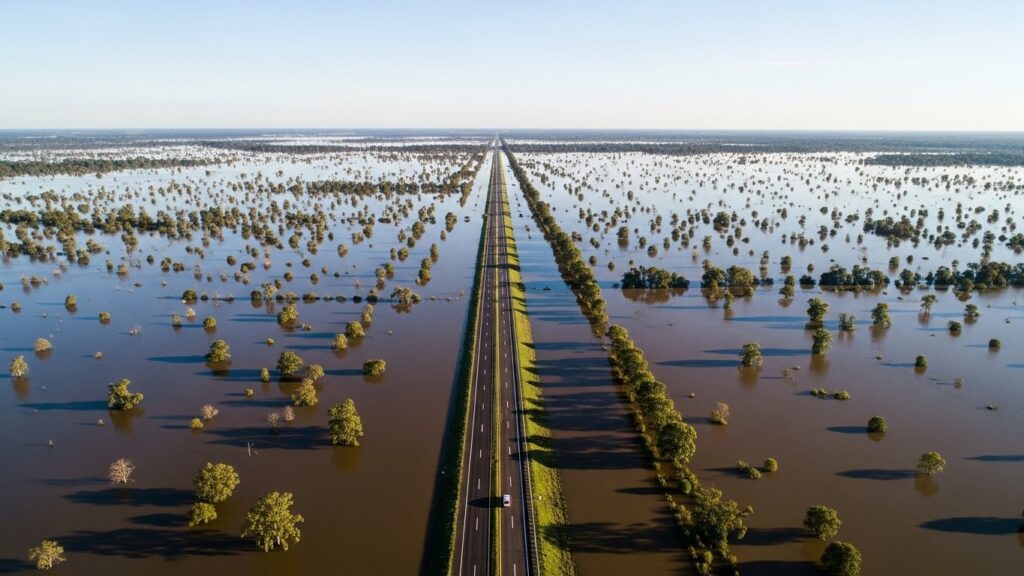
Climate change has led to an increase in extreme weather events, including heatwaves, floods, and tornadoes. These events disrupt local economies, destroy infrastructure, and lead to significant financial losses. The frequency of hurricanes and wildfires is also on the rise, causing irreversible damage to communities and costing billions of dollars in recovery.
Long-Term Environmental Changes
Beyond the immediate effects of extreme weather, climate change is driving long-term environmental changes that are altering the global landscape. Rising sea levels threaten coastal cities, while changes in rainfall patterns and droughts affect agricultural output, leading to potential food shortages.
2. Climate Change and Economic Sectors
Agriculture: Impact on Crop Yields and Food Security
Agriculture is one of the most climate-sensitive industries. Rising temperatures, shifting rainfall patterns, and extreme weather events are already affecting crop yields, particularly in regions that rely on rain-fed agriculture. As climate change intensifies, food security will become an increasingly important issue.
The Impact of Extreme Weather on Crop Yields
Droughts, floods, and unseasonably warm temperatures disrupt planting cycles and damage crops, resulting in lower harvests. This not only leads to increased food prices but also threatens the livelihoods of farmers and agricultural workers worldwide.
The Shift Towards Climate-Resilient Crops
In response to these challenges, there is a growing focus on developing climate-resilient crops that can withstand harsher conditions. Advances in genetic engineering, along with sustainable farming practices, offer potential solutions to mitigate the impact of climate change on agriculture.
Energy: Shifting from Fossil Fuels to Renewables
The energy sector is also undergoing significant transformation due to climate change. With growing concerns about the environmental impact of fossil fuels, there has been a global shift toward renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and hydropower.
The Growing Demand for Clean Energy
Countries around the world are increasingly investing in renewable energy technologies to reduce carbon emissions and transition to a sustainable energy future. As renewable energy becomes more affordable and efficient, it’s expected to continue replacing fossil fuels, reshaping the global energy market.
Impact of Weather Patterns on Energy Supply
Climate change is also affecting the availability and reliability of energy sources. Changes in weather patterns can impact hydropower generation, with droughts reducing water availability for dams. Similarly, extreme temperatures lead to higher energy demand for cooling and heating, straining energy grids.
3. The Financial Cost of Climate Change
The Economic Cost of Natural Disasters
The financial burden of climate-related disasters is immense. In recent years, natural disasters have caused trillions of dollars in damages globally. The destruction of infrastructure, homes, and businesses leads to significant economic loss, especially in developing countries.
Infrastructure Damage and Recovery Costs
In addition to immediate disaster recovery costs, countries must invest in rebuilding infrastructure to make it more resilient to future events. These investments are crucial but often require massive financial resources that could be better used for development purposes.
Investing in Resilience and Recovery Plans
To minimize the long-term impact of climate change, governments and businesses must invest in resilience strategies. These include building climate-resilient infrastructure, updating urban planning policies, and developing disaster preparedness plans to reduce the financial toll of future events.
4. Global Trade and Climate Change
Disruptions to Global Supply Chains
Climate change is also disrupting global supply chains. Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, and wildfires, are damaging production facilities and transportation networks, causing delays in the production and delivery of goods.
Impact on International Trade Routes and Ports
Rising sea levels and storm surges threaten global trade routes, particularly in coastal regions. Ports that are vital for international trade may become submerged, forcing businesses to find new, often more expensive, ways to transport goods.
How Climate Change Affects Trade Competitiveness
As climate change impacts the cost and efficiency of global trade, businesses in vulnerable regions may face increased production costs, making it harder for them to compete in the global marketplace. Trade policies may need to be adjusted to account for these risks.
5. Climate Change and Employment
Job Losses in Climate-Vulnerable Industries
Certain industries, particularly agriculture, tourism, and fossil fuels, are highly vulnerable to climate change. As these industries struggle to adapt to environmental shifts, workers may face job losses and economic instability.
Green Jobs: The Growth of Sustainable Employment
On the flip side, the transition to a green economy is creating new opportunities in renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and environmental protection. Governments and businesses are increasingly investing in green jobs, which provide sustainable career opportunities while addressing environmental challenges.
Training and Transitioning the Workforce
As industries adapt to a changing climate, workers in vulnerable sectors need support through retraining programs and transition assistance. This ensures that the workforce remains competitive in an increasingly green economy.
6. Climate Change Mitigation: Strategies and Solutions
Carbon Tax and Emission Reduction Policies
To tackle the economic impacts of climate change, governments are introducing policies like carbon taxes and emission reduction targets. These initiatives incentivize businesses to reduce their carbon footprint and invest in more sustainable practices.
Sustainable Agriculture and Resource Management
Sustainable agriculture practices, such as crop rotation, organic farming, and water-efficient irrigation systems, help mitigate the environmental impact of farming. These practices are becoming more mainstream as businesses and governments recognize the importance of protecting natural resources for future generations.
Innovative Technologies for Carbon Capture and Storage
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies are playing an important role in reducing carbon emissions. These technologies capture CO2 emissions from industrial processes and store them underground, preventing them from entering the atmosphere.
The Role of Governments and Corporations in Mitigation
Both governments and corporations have critical roles to play in climate change mitigation. Governments must enact policies that incentivize sustainable practices, while corporations must integrate sustainability into their core strategies to reduce their environmental impact.
7. The Role of International Cooperation in Addressing Climate Change
Global Agreements and Treaties: The Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement, a global treaty signed by nearly 200 countries, is a pivotal step in addressing climate change. It sets targets for reducing global emissions and increasing global temperature limits, aiming to limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
The Importance of International Funding for Climate Action
Developing countries often lack the resources to tackle climate change effectively. International funding and climate financing are crucial to supporting these countries’ adaptation efforts and ensuring that climate change is addressed globally.
Cross-Border Collaboration on Climate Solutions
Climate change is a global issue that requires a unified response. International cooperation is essential for developing and implementing effective solutions that benefit all nations, regardless of their economic standing.
Conclusion
The impact of climate change on global economies is profound and far-reaching. From disruptions in supply chains to shifts in agricultural productivity and rising costs from natural disasters, businesses and governments alike must act quickly to mitigate its effects. By adopting sustainable practices, investing in clean technologies, and collaborating internationally, we can build a more resilient future that minimizes the economic burden of climate change.
FAQs
1. How does climate change affect global trade?
Climate change can disrupt supply chains, damage infrastructure, and threaten trade routes, leading to increased costs and delays in global commerce.
2. What is the role of renewable energy in combating climate change?
Renewable energy helps reduce reliance on fossil fuels, lowering greenhouse gas emissions and supporting a sustainable, low-carbon economy.
3. How can businesses prepare for the financial costs of climate change?
Businesses can prepare by investing in climate-resilient infrastructure, adopting sustainable practices, and diversifying operations to mitigate risks associated with climate change.
4. What are the economic impacts of climate change on agriculture?
Climate change affects crop yields, food security, and water availability, leading to higher food prices and potential supply shortages.
5. How can AI help in addressing climate change?
AI can help optimize energy use, predict climate-related risks, and develop sustainable solutions for agriculture, transportation, and other sectors.